Managing Urban Heat Under Climate Change
Project Overview
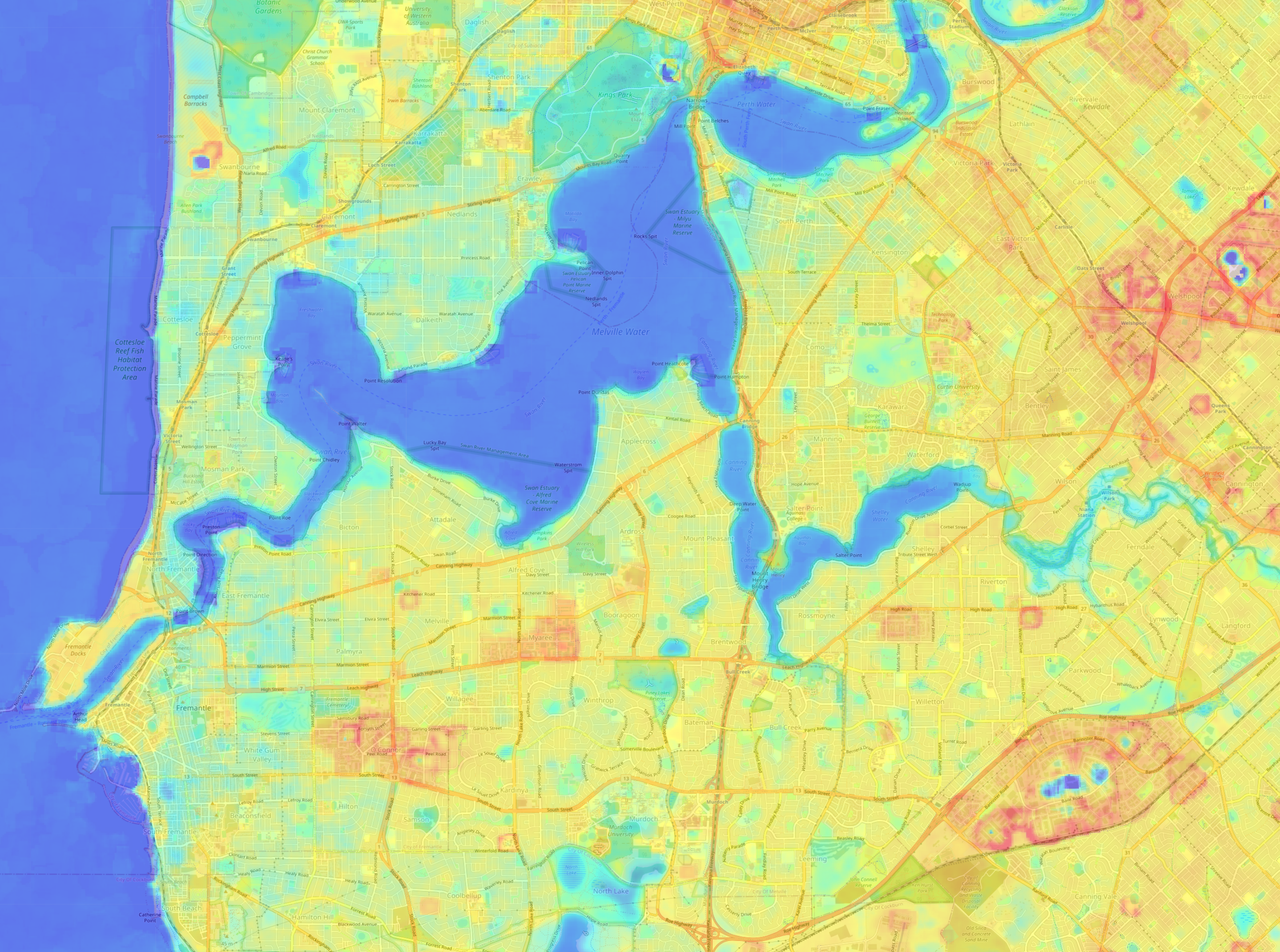
Since 1900, heatwaves have claimed more lives in Australia than any other natural hazard, with the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect significantly contributing to this trend. The UHI effect, a phenomenon where urban areas register significantly higher temperatures than their rural counterparts due to human activities and modifications like roads, concrete, and buildings, plays a critical role in this trend, and is expected to intensify with climate change, leading to more frequent and severe heatwaves. This will have serious implications for public health, economic stability, and urban quality of life, highlighting the urgent need for proactive measures to protect urban populations.
In collaboration with BMT Commercial Australia, we developed a software solution to address the pressing issue of UHI in the context of climate change. This project leverages remote sensing technology to provide actionable insights for urban heat management.
Our tool offers the following key functionalities:
- Automated Data Acquisition: Based on user-specified latitude, longitude, and duration, the tool automatically downloads raw Landsat 8 satellite images from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) database.
- NDVI Calculation: The tool processes the images to calculate the Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), essential for assessing vegetation health and coverage.
- LST Calculation: It computes the Land Surface Temperature (LST) from the satellite imagery, providing critical data on surface heat distribution.
- UHI Analysis: By integrating NDVI and LST data, the tool calculates the Urban Heat Island effect for the specified region of interest.
Through processing satellite data—including cloud filtering, shadow masking, and environmental metric calculations, the study identified the thermal disparities between urban and rural areas, highlighting the impact of urbanisation on local climates.
By combining these functionalities, the tool enables urban planners, environmental scientists, and policymakers to:
- Identify and Monitor Hotspots: Detect areas of intense heat accumulation and monitor changes over time.
- Assess Vegetation Impact: Understand the role of vegetation in mitigating urban heat and plan green infrastructure accordingly.
- Inform Policy and Planning: Provide data-driven insights to support the development of effective urban heat management strategies.
Additionally, this software solution offers valuable insights for climate change studies, enabling continuous monitoring of how urbanisation shapes local and regional climates.
Involved Organisations
- BMT Commercial Australia
- Australian Space Data Analysis Facility (ASDAF)
Industry Sector
- Engineering
- Consultancy
Services Rendered
- Access to Data
- Specialised Data Analytics
- Data Engineering
- Consulting
- Training
Other Projects
Eyes on Australian Forests
The Eyes on Australian Forests tool addresses a significant need by empowering specialist users who lack extensive programming experience or familiarity with APIs.
Ecocene
Ecocene developed Emapper, a cloud-based environmental data platform that allows users to consolidate data and analytics to plan activities for improved environmental and management decision-making and outcomes.
Desert Fireball Network (DFN), Curtin University
A powerful tool to automatically query and visualise himawari data at known fireball locations.



